Understanding RT-PCR: A Gold Standard in Molecular Diagnostics
Introduction
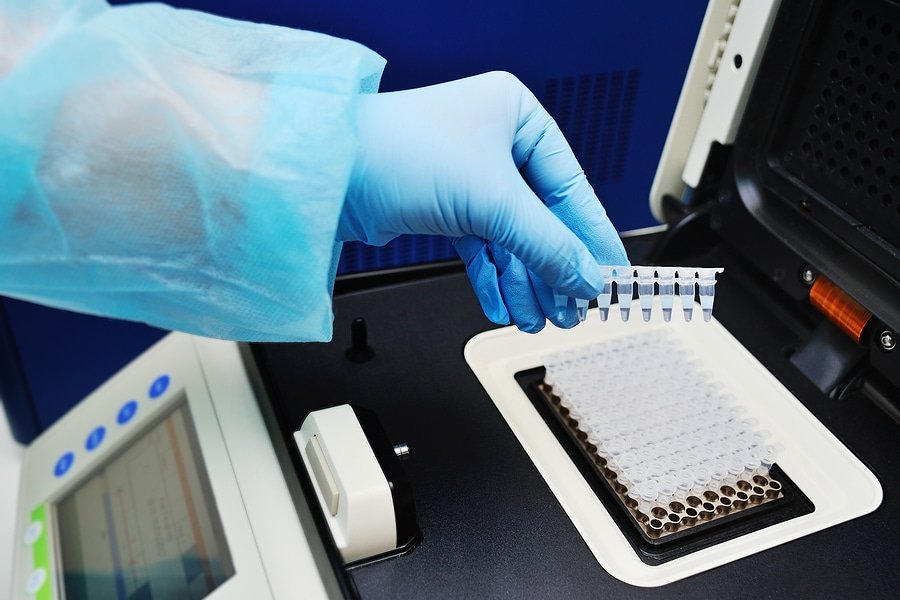
Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) has revolutionized the field of molecular diagnostics. Originally developed in the early 1980s, this technique has become a cornerstone for detecting RNA viruses, cancer biomarkers, and genetic disorders with high precision and speed. Its application gained global attention during the COVID-19 pandemic, but its clinical utility extends far beyond.
What is RT-PCR?
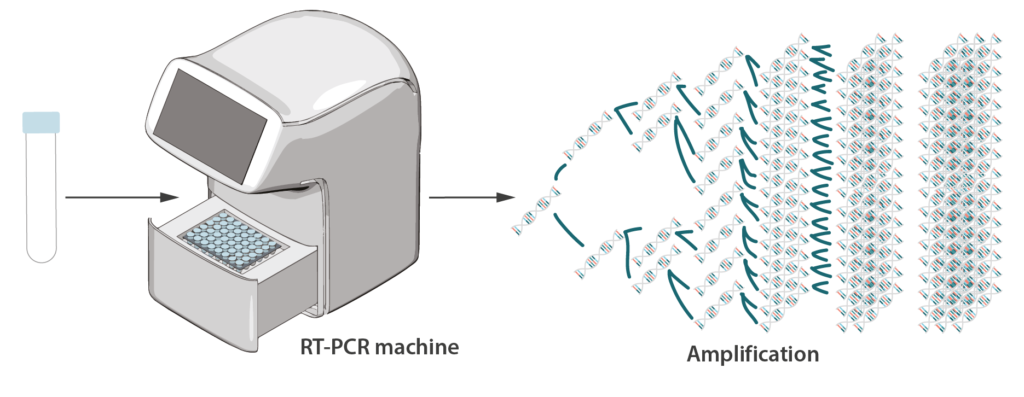
RT-PCR, or Reverse Transcription PCR, is a laboratory technique used to detect and quantify RNA. It combines two critical steps:
- Reverse Transcription (RT): Converts RNA into complementary DNA (cDNA) using the reverse transcriptase enzyme.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): Amplifies the cDNA to detectable levels using DNA polymerase and specific primers.
This powerful combination enables the detection of even minute quantities of RNA, making RT-PCR extremely sensitive and specific.
Key Applications of RT-PCR in Diagnostics
1. Infectious Disease Detection
RT-PCR is a gold-standard test for detecting RNA viruses such as:
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- HIV
- Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
- Influenza
It provides early diagnosis, which is crucial for treatment and preventing disease transmission.
2. Cancer Diagnostics
Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) helps detect gene expression changes associated with various cancers (e.g., breast, leukemia, and colorectal). It can identify:
- Tumor markers
- Oncogenes
- Fusion transcripts
3. Genetic and Hereditary Disorders
RT-PCR helps in identifying genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities. It plays a role in diagnosing:
- Thalassemia
- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
- Fragile X syndrome
4. Personalized Medicine
RT-PCR enables gene expression profiling, allowing doctors to tailor treatment plans based on a patient’s genetic makeup or tumor biology.
Benefits of RT-PCR in Clinical Diagnostics
- ✅ High Sensitivity and Specificity – Detects even low-abundance RNA.
- ✅ Rapid Results – Some platforms offer results within hours.
- ✅ Quantitative Analysis – Measures the amount of RNA, aiding in disease monitoring.
- ✅ Multiplexing Capability – Detects multiple pathogens in a single reaction.
Importance During the COVID-19 Pandemic
RT-PCR was globally adopted for SARS-CoV-2 detection. It became a crucial tool for:
- Early case identification
- Isolation and contact tracing
- Monitoring viral load during treatment
This highlighted its scalability, accuracy, and role in pandemic preparedness.
Limitations and Considerations
While RT-PCR is powerful, it requires:
- Skilled personnel
- Stringent quality control
- Expensive reagents and instruments
False positives or negatives can occur due to contamination or improper sample handling, making validation critical.
Conclusion
RT-PCR continues to be a cornerstone technology in molecular diagnostics, enabling early and accurate detection of a wide range of diseases. As advancements continue, including integration with digital health tools and automation, RT-PCR will remain an essential tool in precision medicine and global health.