Understanding Bio CLIA Instruments: Importance and Working Mechanism in Modern Diagnostics
Introduction
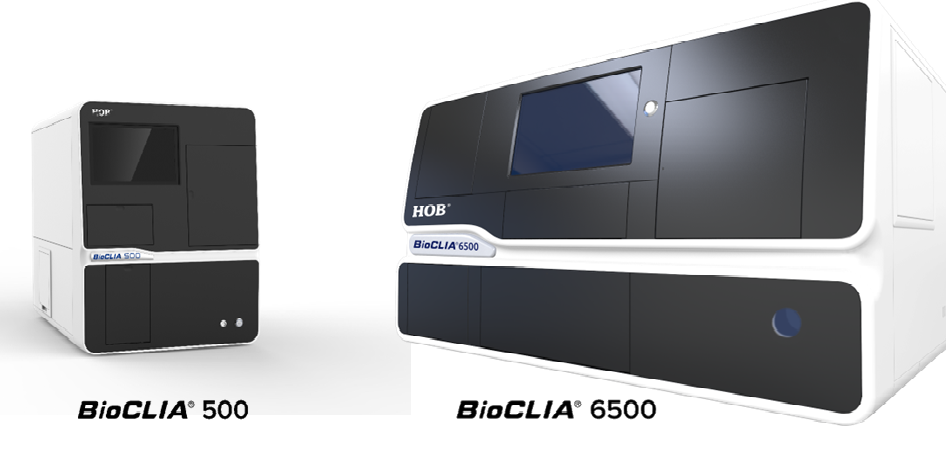
In the ever-evolving field of clinical diagnostics, Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA) has emerged as a revolutionary technology, combining high sensitivity, specificity, and speed. Among the most reliable tools utilizing this technique are Bio CLIA Instruments—automated systems designed to perform a broad range of immunoassays for various clinical applications, including infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, allergies, hormones, and tumor markers.
This blog explores the importance of Bio CLIA instruments in modern healthcare settings and dives into their working mechanism to help laboratories and clinicians understand their value.
Why Bio CLIA Instruments Matter
- High Sensitivity and Specificity
CLIA technology offers superior sensitivity, often detecting analytes at picogram levels. This is critical for early disease detection and monitoring. - Automation and Throughput
Bio CLIA systems are fully automated, reducing manual errors and ensuring consistency. They can process dozens to hundreds of samples per hour, making them ideal for medium to high-throughput laboratories. - Wide Test Menu
These instruments support a wide array of tests—from thyroid and reproductive hormones to infectious disease panels and tumor markers—making them versatile solutions in diagnostic settings. - Faster Turnaround Time
With high-speed processing and minimal incubation periods, Bio CLIA instruments significantly reduce the time from sample loading to result delivery, enabling faster clinical decision-making. - Reagent Rental Model
Many suppliers offer the instruments on a reagent rental basis, allowing labs to install high-end analyzers with minimal upfront investment and pay based on reagent consumption.
Working Mechanism of Bio CLIA Instruments
The Bio CLIA system functions based on the principle of chemiluminescence, where a chemical reaction produces light. Here’s a simplified step-by-step breakdown:
1. Sample and Reagent Preparation
The sample (usually serum or plasma) is automatically pipetted into a reaction cuvette along with magnetic microbeads coated with specific antibodies.
2. Antigen-Antibody Binding
If the target analyte is present in the sample, it binds with the antibody-coated microbeads, forming a stable immune complex.
3. Washing Steps
Unbound substances are removed through a series of automated washing steps using magnetic separation, ensuring high assay purity.
4. Chemiluminescent Substrate Addition
A substrate containing a chemiluminescent label (usually acridinium or isoluminol) is added. Upon triggering, the substrate emits light as part of a chemical reaction.
5. Signal Detection
The emitted light is detected by a photomultiplier tube (PMT) or optical sensor within the instrument. The intensity of light is directly proportional to the amount of analyte in the sample.
6. Result Interpretation and Reporting
The instrument’s software processes the signal, compares it to calibration curves, and provides a quantitative or qualitative result based on the test being run.
Applications in Clinical Diagnostics
- Thyroid Panel (TSH, FT3, FT4)
- Fertility & Reproductive Hormones (LH, FSH, Progesterone, Estradiol)
- Infectious Disease Markers (HBsAg, HIV, HCV)
- Tumor Markers (AFP, CEA, CA-125)
- Autoimmune and Allergy Testing
Conclusion
Bio CLIA instruments are a cornerstone of modern laboratory diagnostics, offering the perfect blend of precision, efficiency, and versatility. With the increasing demand for rapid, reliable, and high-throughput testing, CLIA-based systems are proving indispensable in hospitals, diagnostic chains, and research institutions.
Whether you’re planning to upgrade your existing analyzer or expand your diagnostic capabilities, adopting a Bio CLIA system could be a smart move toward future-ready healthcare diagnostics.