Understanding qPCR: A Cornerstone in Modern Clinical Diagnostics
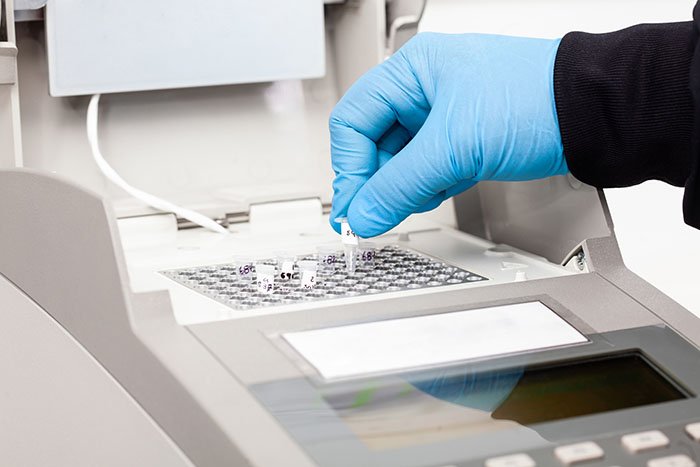
In today’s fast-evolving field of molecular diagnostics, quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) – also known as real-time PCR – plays a pivotal role in the accurate detection and quantification of nucleic acids. From infectious disease diagnosis to cancer research, the qPCR machine has become an indispensable tool in clinical laboratories and research institutions.
What is qPCR?
qPCR (quantitative PCR) is an advanced molecular biology technique that amplifies and simultaneously quantifies a targeted DNA molecule. Unlike conventional PCR, which only indicates the presence or absence of a target sequence after the reaction, qPCR provides real-time monitoring of the amplification process, allowing both detection and precise quantification.
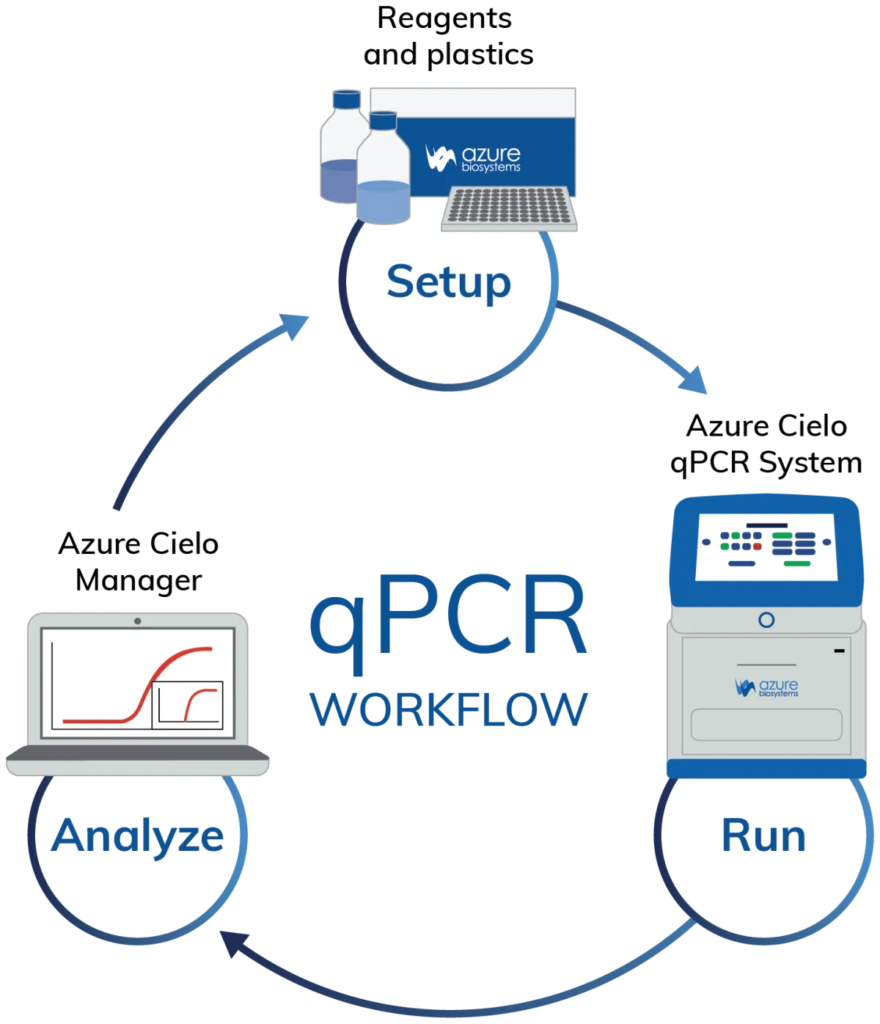
Working Principle of a qPCR Machine
A qPCR machine works by combining thermal cycling with fluorescent dye chemistry. During the amplification, fluorescent signals are emitted and measured in real-time by the instrument. This allows for:
- Quantification of nucleic acids (DNA/RNA)
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Rapid turnaround time
Fluorescent signals increase proportionally to the amount of DNA being amplified, and this is plotted in real-time to generate amplification curves, which help in analyzing the initial quantity of the target gene.
Clinical Significance and Applications
The clinical relevance of qPCR is profound due to its accuracy, speed, and versatility. Some of its key applications include:
1. Infectious Disease Detection
qPCR enables rapid detection of pathogens such as:
- COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2)
- HIV, HBV, HCV
- Tuberculosis and Influenza viruses
Its high sensitivity allows detection even when pathogen load is very low, enabling early diagnosis and timely treatment.
2. Cancer Diagnostics and Prognosis
qPCR is used for:
- Detecting oncogenes or tumor suppressor gene mutations
- Quantifying circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)
- Evaluating gene expression profiles to aid personalized treatment plans
3. Genetic and Inherited Disorders
It is a powerful tool for:
- Carrier screening
- Prenatal diagnostics
- Detection of gene mutations linked to inherited diseases
4. Pharmacogenomics and Drug Response
qPCR helps in assessing gene variants that affect drug metabolism, guiding clinicians to make more effective and safer therapeutic decisions.
5. Transplantation Monitoring
It is used for monitoring viral reactivation or host immune response post-transplantation, especially for cytomegalovirus (CMV) or Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Why qPCR is Preferred in Clinical Settings
- ✅ High Sensitivity and Specificity
- ✅ Real-time Results
- ✅ Low Sample Volume Requirement
- ✅ Quantitative Accuracy
- ✅ Fast Turnaround Time
- ✅ Wide Diagnostic Applications
Conclusion
The qPCR technique and qPCR machines are transforming modern diagnostics by offering precise, fast, and reliable results. As personalized medicine and early detection become more critical in healthcare, qPCR continues to expand its role across various clinical domains.
Investing in advanced qPCR platforms ensures laboratories are equipped to meet current and future diagnostic challenges with confidence and efficiency.