Is the 17-OHP ELISA for CAH Newborn Screening?
17-OHP ELISA is the mandatory newborn screening test for CAH. Learn why structured screening prevents adrenal crisis and how Amindo enables life-saving NICU diagnostics.
Why 17-OHP Is No Longer an “Optional” Endocrine Test?
Endocrine diagnostics has undergone a structural shift. Hormone testing is no longer ordered merely to “confirm suspicion.” It is increasingly deployed as a preventive diagnostic gate — a biochemical firewall that identifies life-threatening disease before collapse, hospitalization, or irreversible morbidity.

No marker illustrates this transition more clearly than 17-Hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP).
17-OHP is not simply another adrenal hormone parameter. It is the primary biochemical gatekeeper for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) — a disorder that remains one of the most preventable causes of neonatal shock, misdiagnosed sepsis, and avoidable infant death worldwide.
As newborn screening programs expand, infertility clinics grow, and adrenal disorders are more aggressively managed, accurate, standardized, and scalable measurement of 17-OHP has become non-negotiable.
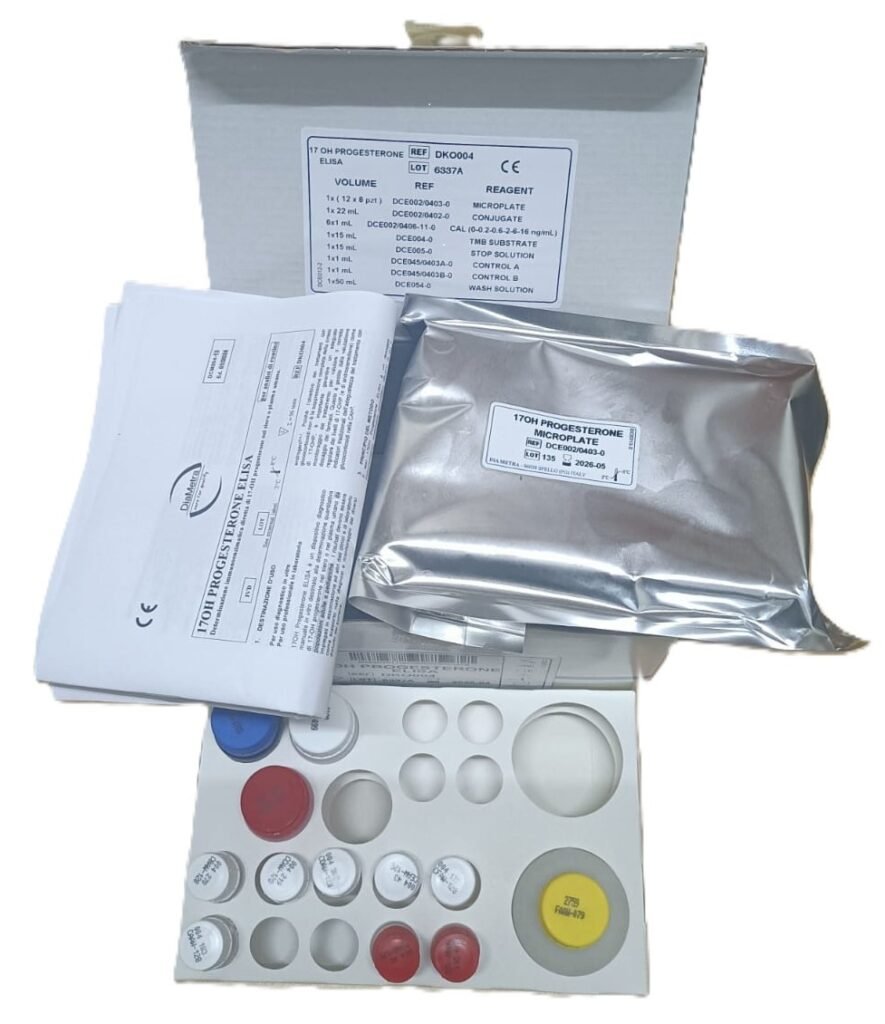
Amindo Biologics supplies CE-marked, globally validated DiaMetra 17-OHP ELISA kits, enabling laboratories to implement high-confidence, high-throughput endocrine screening and monitoring workflows.
What Is 17-Hydroxyprogesterone?
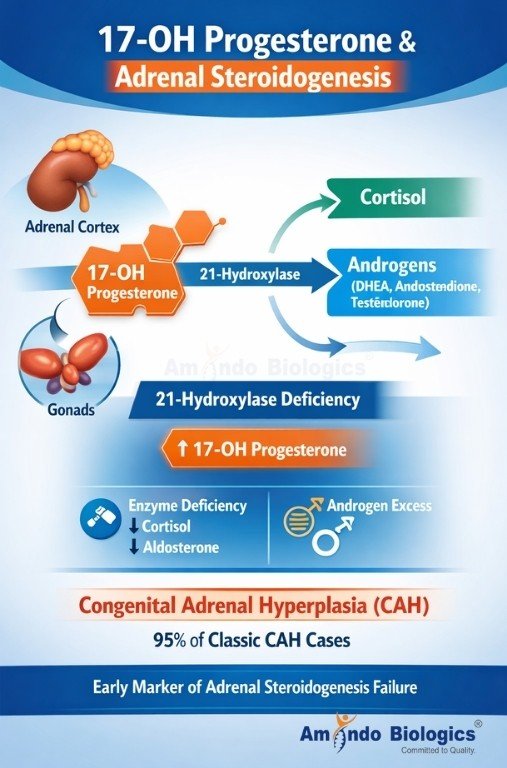
17-OHP is a steroid precursor produced in the adrenal cortex and gonads during the biosynthesis of:
• Cortisol
• Androgens (DHEA, androstenedione, testosterone)
Under normal physiology, 17-OHP is rapidly converted into cortisol through the action of 21-hydroxylase and related enzymes.
When these enzymes are deficient, 17-OHP accumulates — making it the earliest biochemical footprint of adrenal steroidogenesis failure.
This accumulation is the hallmark of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) — particularly 21-hydroxylase deficiency, which accounts for over 95% of classic CAH cases worldwide.
Is Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia More Common Than We Think?
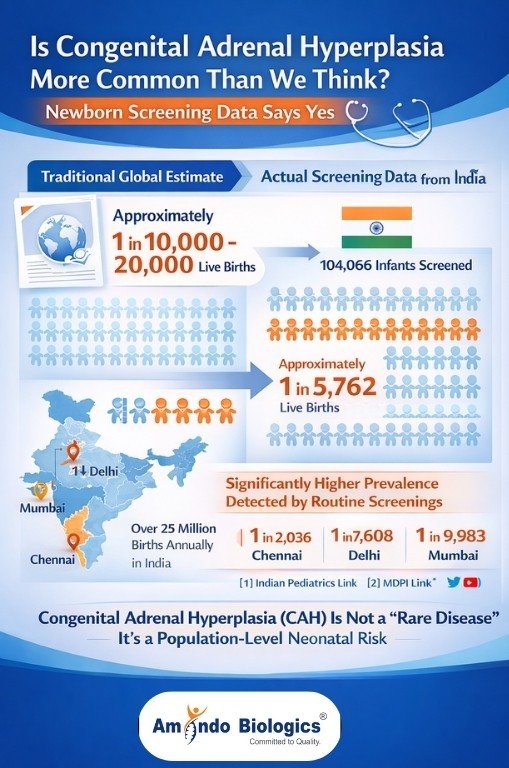
Traditional global estimates place classic CAH prevalence at approximately 1 in 10,000–20,000 live births.
However, structured newborn screening cohorts demonstrate significantly higher detection rates when systematic screening is applied.
A large Indian newborn screening study involving 104,066 infants reported a screen-positive CAH incidence of approximately 1 in 5,762 births, with major regional variability — including rates as high as 1 in 2,036 in Chennai, and 1 in 7,608 in Delhi and 1 in 9,983 in Mumbai.
(Source: Indian Pediatrics; MDPI)
https://www.indianpediatrics.net/jan2020/49.pdf
https://www.mdpi.com/2409-515X/6/3/70
These data establish CAH as a population-level neonatal risk rather than a rare disorder, particularly in high-birth-volume countries like India (>25 million births annually).
Why 17-OHP Screening Is Mandatory, Not Optional

Multiple international public health authorities classify 17-OHP as the mandatory first-tier newborn screening marker for CAH, including programs in the US, UK, EU, and Australia.
Newborn screening studies show that early biochemical identification:
• Prevents salt-wasting adrenal crisis
• Reduces neonatal morbidity and mortality
• Eliminates recurrent NICU admissions
• Prevents unnecessary antibiotic exposure
• Preserves neurodevelopmental outcomes
(Source: Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición; PMC)
https://www.elsevier.es/en-revista-endocrinologia-diabetes-nutricion-english-ed–413-articulo-newborn-screening-congenital-adrenal-hyperplasia-S2530018018300088
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10620452/
Without screening, CAH is usually detected only after adrenal collapse has begun.
Why Preterm False-Positive Problem Is a Workflow Issue, Not a Test Limitation?
Preterm and low-birth-weight infants exhibit physiologically elevated 17-OHP levels due to adrenal immaturity, increasing false-positive rates if unstratified cut-offs are applied.
(Source: Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism; PMC)
https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/104/8/3172/5374693
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7569755/
However, gestational age- and birth-weight-adjusted cut-offs with reflex confirmatory workflows markedly improve screening specificity and positive predictive value — while preserving high sensitivity.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8006248/
This confirms that false positives reflect unstructured laboratory workflows — not limitations of 17-OHP as a screening gate.
Why ELISA Is the Global Standard Platform
ELISA is the preferred platform for population-level endocrine diagnostics because it offers:
• Quantitative cut-off reporting
• High analytical reproducibility
• Batch-to-batch standardization
• High throughput
• LIS integration & reflex workflows
• Cost efficiency
• Automation compatibility
These features are critical for newborn screening, NICU diagnostics, and high-volume endocrine laboratories.
Why DiaMetra 17-OHP ELISA via Amindo Biologics

Amindo supplies globally validated DiaMetra CE-marked ELISA kits offering:
Key Advantages
✔ High sensitivity & specificity
✔ Excellent correlation with reference LC-MS/MS
✔ Serum & plasma compatible
✔ CE-marked IVD
✔ Stable reagents & robust calibration
✔ Clear SOP & automation adaptability
✔ Full technical & application support

You are not purchasing a kit —https://amindobiologics.com/our-products/
You are installing a neonatal endocrine safety gate.
Which Laboratories & Institutions Uses This Kit?
• Newborn screening labs
• NICU-attached hospital labs
• Endocrinology reference labs
• Fertility centers
• Government screening programs
• Corporate hospital chains
• Academic & research institutions
What Are The Clinical & Health-System Impact?
| For Patients | For Hospitals |
| Prevents adrenal crisis | Reduces NICU stays |
| Prevents infant death | Prevents litigation |
| Enables early therapy | Improves medico-legal defensibility |
| Reduces hospital readmissions | Improves diagnostic yield |
| Preserves growth & cognition | Improves margins |
FAQs:
FAQ 1. Why must every NICU include 17-OHP screening?
Because salt-wasting CAH mimics sepsis and collapse occurs before diagnosis. 17-OHP is the only preventive biochemical gate.
FAQ 2. Why ELISA instead of random chemistry or CLIA?
Because ELISA provides structured, standardized, quantitative population screening workflows.
FAQ 3. Which Amindo products form a complete CAH workflow?
| Diagnostic Gate | Amindo Product |
| Screening | 17-OHP ELISA |
| Confirmation | ACTH |
| Functional | Cortisol |
FAQ 4. Is CAH screening cost-effective?
Yes — one ELISA screen costs less than a single NICU admission.
FAQ 5. Can Amindo support stratified newborn cut-offs?
Yes — workflows support gestational age & birth-weight adjusted interpretation.
17-OHP is no longer an optional endocrine parameter.
It is a neonatal safety gate, a fertility work-up differentiator, and a hospital risk-management tool.
With DiaMetra 17-OHP ELISA via Amindo Biologics, laboratories implement structured, defensible, and life-saving endocrine diagnostics.
Every NICU without structured 17-OHP ELISA screening is operating without a neonatal safety net.
We just do not sell hormone kits.
We architect endocrine diagnostic safety nets.
At Amindo Biologics, we enable structured, life-saving neonatal endocrine diagnostics.
Our 17-OHP ELISA, ACTH, and Cortisol assays provide standardized, high-performance newborn screening and reflex confirmation — supporting early detection of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, reduced diagnostic ambiguity, medico-legal defensibility, and confident NICU decision-making.